36 Views
top of page
POCUS
Public·149 members
All topics
AI (1)
Allergy/immunology (2)
Cardiology (15)
Critical Care Medicine (12)
EKGs (3)
Endocrinology (0)
Gastrointestinal (6)
General Medicine (15)
Hematology (4)
Imaging (27)
Infectious Disease (32)
MCQs (41)
Metabolism (4)
Nephrology (2)
Neurology (10)
Obesity (1)
Oncology (2)
POCUS (21)
Pulmonary (31)
Rhumatology (0)
Statistics (2)
TriviaTuesday (7)
Lung US (2)
LE US (1)
Echocardiography (4)
Lung (0)
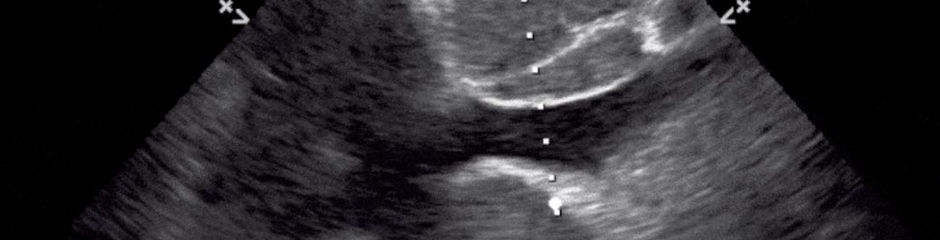
Pericardia Effusion
Mild to moderate pericardial effusion with no obvious collapse of RV during diastole.
32 Views


From the echocardiographic images:
LVOT diameter (D) = 2.56 cm
LVOT area (A) = π × (D/2)² = 3.14 × (1.28)² ≈ 5.15 cm²
LVOT VTI = 11.8 cm
66 Views
Members
- Mayada Ali
Pioneer
- saada aladawi
Ali Alkhaldi Ali Alkhaldi
bottom of page



