CRITICAL CARE TRIALS
Stay ahead of the curve with exciting new clinical trials from the critical care field presented in vivid, visual abstract format. Gain comprehensive and insightful perspectives as each critical development is delivered to you.
Jun 12, 2024
BLING III
Continuous vs Intermittent β-Lactam Antibiotic Infusions in Critically Ill Patients With Sepsis
The BLING III trial compared continuous versus intermittent β-lactam infusions (piperacillin-tazobactam or meropenem) in 7031 critically ill sepsis patients. Continuous infusion showed no statistically significant reduction in 90-day mortality (24.9% vs. 26.8%, OR 0.91, 95% CI 0.81–1.01, p=0.08) but achieved higher clinical cure at 14 days (55.7% vs. 50.0%). Secondary outcomes, including ICU and hospital mortality, were similar. Continuous infusion may improve infection resolution, but its mortality benefit remains inconclusive. Practical considerations and resource availability should guide administration strategies
916
Jun 12, 2024
PROTECTION
A Randomized Trial of Intravenous Amino Acids for Kidney Protection
This multicenter RCT evaluated intravenous amino acid infusion versus placebo in 3511 adults undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Amino acids reduced AKI incidence per KDIGO criteria (26.9% vs. 31.7%; RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.77–0.94, p=0.002) and Stage 3 AKI (1.6% vs. 3.0%; RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.35–0.87). Kidney-replacement therapy use was slightly lower (1.4% vs. 1.9%). Secondary outcomes and adverse events showed no significant differences. Findings suggest amino acids may reduce AKI risk in this high-risk population but have limited impact on broader outcomes.
80
Jan 22, 2024
REGARD-VAP
Individualized, short-course antibiotic treatment versus usual long-course treatment for ventilator-associated pneumonia.
This phase 4, open-label trial evaluated short-course (≤7 days) versus usual care (≥8 days) antibiotics in 461 adults with ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). The 60-day composite outcome of death or pneumonia recurrence was similar between groups (41% vs. 44%), confirming non-inferiority. Antibiotic side effects were significantly lower in the short-course group (8% vs. 38%). Median antibiotic duration was 6 days (IQR 5–7) in the short-course group versus 14 days (IQR 10–21) in usual care. Findings support short-course antibiotic therapy as safe and effective for VAP.
763
Nov 29, 2023
The NICO Trial
Effect of Noninvasive Airway Management of Comatose Patients With Acute Poisoning
This study evaluated conservative airway management versus routine tracheal intubation in 225 comatose patients (GCS <9) with suspected acute poisoning. No in-hospital deaths occurred in either group. The conservative strategy showed clinical benefit (win ratio 1.85, 95% CI 1.33–2.58) with fewer adverse events (6% vs. 14.7%, absolute risk difference 8.6%) and pneumonia cases (6.9% vs. 14.7%, absolute risk difference −7.8%). These findings suggest withholding intubation may improve outcomes in select patients without increasing mortality risk.
466
Nov 11, 2023
The MINT Trial
Restrictive or Liberal Transfusion Strategy in Myocardial Infarction and Anemia
This RCT evaluated liberal (Hb <10 g/dL) versus restrictive (Hb <7–8 g/dL) transfusion strategies in 3504 patients with myocardial infarction and anemia (Hb <10 g/dL). The primary outcome (MI or death at 30 days) was similar (16.9% vs. 14.5%; RR 1.15, 95% CI 0.99–1.34, p=0.07). Mortality (9.9% vs. 8.3%) and MI rates (8.5% vs. 7.2%) trended higher in the restrictive group. Findings suggest no significant benefit of liberal transfusion but highlight potential risks of restrictive strategies. Tailored transfusion thresholds are recommended for this high-risk population
550
Oct 25, 2023
AMIKINHAL Trial
Inhaled Amikacin to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
This multicenter RCT assessed inhaled amikacin (20 mg/kg daily for 3 days) versus placebo in 847 mechanically ventilated adults (>72 hours). Inhaled amikacin significantly reduced ventilator-associated pneumonia incidence (15% vs. 22%; p=0.004) and infection-related complications. Adverse effects were slightly higher in the amikacin group but not significantly so. Findings suggest inhaled amikacin as a preventive measure in critically ill ventilated patients, though benefits must be weighed against potential risks. Longer-term outcomes require further study.
291
Oct 14, 2023
The ACRON Trial
Cefepime vs Piperacillin-Tazobactam in Adults Hospitalized with Acute Infection
This study compared Cefepime and Piperacillin-Tazobactam in 2511 hospitalized adults requiring antipseudomonal antibiotics. Rates of stage 3 acute kidney injury (7.0% vs. 7.5%) and mortality (7.6% vs. 6.0%) were similar between groups. However, patients on Cefepime had more neurological dysfunction, with fewer days alive and free of delirium or coma (11.9 vs. 12.2 days). Findings suggest equivalent kidney injury and mortality risks but highlight Cefepime’s association with increased neurotoxicity, guiding antibiotic selection in critically ill patients.
186
Aug 26, 2023
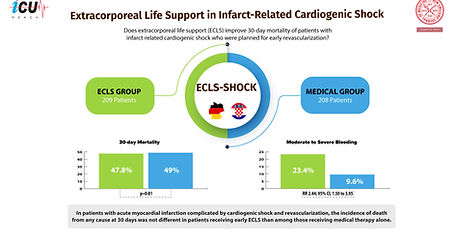
ECLS-SHOCK
Extracorporeal Life Support in Infarct-Related Cardiogenic Shock
This multicenter RCT evaluated early extracorporeal life support (ECLS) plus usual care versus usual care alone in 417 patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. At 30 days, mortality was similar (47.8% vs. 49.0%; RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.80–1.19, p=0.81). ECLS increased mechanical ventilation duration (median 7 vs. 5 days), bleeding (23.4% vs. 9.6%; RR 2.44), and vascular complications (11.0% vs. 3.8%; RR 2.86). The study suggests that early routine ECLS does not improve survival and may increase complications, requiring careful patient selection.
156
Jul 13, 2023
PATCH Trauma Trial
Prehospital Tranexamic Acid for Severe Trauma
This multicenter RCT evaluated prehospital tranexamic acid (TXA) versus placebo in 1310 adults with major trauma at risk for coagulopathy. Survival with favorable functional outcome at 6 months (primary outcome) was similar between groups (53.7% vs. 53.5%; RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.90–1.12, p=0.95). Fewer patients in the TXA group died within 28 days (statistically significant) but not at 6 months. Serious adverse events were comparable. While TXA did not improve long-term functional outcomes, its early mortality benefit supports further exploration in trauma care
157
Jul 6, 2023
TAME Trial
Mild Hypercapnia or Normocapnia after Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
This multicenter RCT evaluated targeted mild hypercapnia (PaCO₂ 50–55 mm Hg) versus normocapnia (PaCO₂ 35–45 mm Hg) for 24 hours in 1700 comatose adults resuscitated after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. At 6 months, favorable neurologic outcomes were similar (43.5% vs. 44.6%; RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.87–1.11, p=0.76), as were mortality rates (48.2% vs. 45.9%; RR 1.05, 95% CI 0.94–1.16). No significant difference in adverse events was observed. These findings support continuing normocapnia as standard care, as mild hypercapnia does not improve neurologic outcomes or
102
Jun 16, 2023
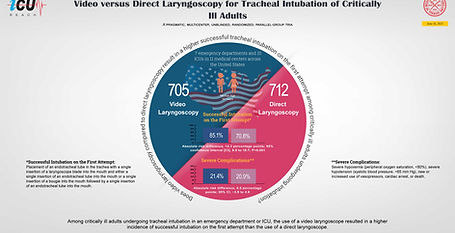
DEVICE Trial
Video versus Direct Laryngoscopy for Tracheal Intubation of Critically Ill Adults
This multicenter RCT compared video laryngoscopy (VL) to direct laryngoscopy (DL) in 1417 critically ill adults undergoing tracheal intubation in emergency departments and ICUs. First-attempt intubation success was higher with VL (85.1% vs. 70.8%; absolute risk difference 14.3%, 95% CI 9.9–18.7, p<0.001). Severe complications were similar between groups. Findings suggest VL improves first-attempt intubation success, particularly for less experienced operators, and supports its routine use in critical care settings.
130
Mar 21, 2023
CAPE-COD
Hydrocortisone in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia
In a phase 3 multicenter RCT of ICU patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia, hydrocortisone significantly reduced 28-day mortality (6.2% vs. 11.9%; absolute difference -5.6%, 95% CI -9.6 to -1.7, P = 0.006). It also lowered rates of intubation (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.40–0.86) and vasopressor use (HR 0.59, 95% CI 0.43–0.82). Rates of hospital-acquired infections and GI bleeding were similar. Hydrocortisone shows promise as an adjunctive therapy in this setting.
453